Authors
Tesfaye Hailemariam Barkae, 1. State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 5625 Renmin Street, Changchun 130022, Jilin,China;2. School of Applied chemistry and Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, Anhui, China;3. Wolkite university, College of Natural & Computational Science, Department of Chemistry, P.O Box 07, Wolkite, Ethiopia;
Mohamed Ibrahim Halawa, 1. State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 5625 Renmin Street, Changchun 130022, Jilin,China;4. Department of Pharmaceutical Analytical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Mansoura University, 35516, Mansoura, Egypt;5. College of Chemistry and Environmental Engineering and College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, Guangdong, China;
Tadesse Haile Fereja, 1. State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 5625 Renmin Street, Changchun 130022, Jilin,China;6. Ambo University, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Department of Pharmacy, P. O. Box 19, Ambo, Ethiopia;
Shimeles Addisu Kitte, 1. State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 5625 Renmin Street, Changchun 130022, Jilin,China;7. Jimma University, College of Natural Sciences, Department of Chemistry, P. O. Box 378, Jimma, Ethiopia;
Xian-Gui Ma, 1. State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 5625 Renmin Street, Changchun 130022, Jilin,China;2. School of Applied chemistry and Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, Anhui, China;
Ye-Quan Chen, 1. State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 5625 Renmin Street, Changchun 130022, Jilin,China;
Guo-Bao Xu, 1. State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 5625 Renmin Street, Changchun 130022, Jilin,China;Follow
Corresponding Author
Xu Guo-Bao(guobaoxu@ciac.ac.cn)
Abstract
Herein, sulfamic acid (SA) was utilized, for the first time, to enhance significantly the luminol electrochemiluminescence (ECL). With the SA concentration increased from 0.1 μmol·L-1 to 500 μmol·L-1 the ECL intensity increased proportionally. The developed luminol/SA ECL system was employed to detect dopamine (DA) based on its prominent quenching effect. The Stern-Volmer equation of Io/I= 1+Ksv[DA] could be applied to express well the quenching mechanism of DA in the luminol/SA ECL system. The calibration plot showed that the increase in the DA concentration from 0.5 to 20 μmol·L-1 decreased linearly the ECL intensity with a detection limit of 30 nmol·L-1. The luminol/SA ECL system was successfully carried out for DA detection in urine real sample by employing the standard addition method with the excellent recoveries of 103% ~ 105%. Selectivity of the as-developed ECL system was also investigated by using uric acid, ascorbic acid, sugars and amino acids. The results indicated that the ECL intensities changed negligibly in the presence of other substances.
Graphical Abstract
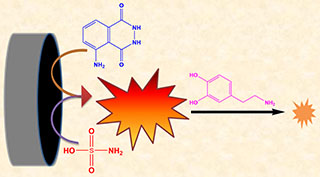
Keywords
electrochemiluminescence, sulfamic acid, luminol, dopamine
Publication Date
2021-04-28
Online Available Date
2021-03-15
Recommended Citation
Tesfaye Hailemariam Barkae, Mohamed Ibrahim Halawa, Tadesse Haile Fereja, Shimeles Addisu Kitte, Xian-Gui Ma, Ye-Quan Chen, Guo-Bao Xu.
Luminol/Sulfamic Acid Electrochemiluminescence and Its Application for Dopamine Detection[J]. Journal of Electrochemistry,
2021
,
27(2): 168-176.
DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.201247
Available at:
https://jelectrochem.xmu.edu.cn/journal/vol27/iss2/5


